In today’s competitive electronics market, companies increasingly turn to contract electronics manufacturing services (CEMS) to ensure high-quality production while keeping costs under control. Whether you’re launching a new product or scaling an existing design, choosing the right electronics manufacturing partner can make the difference between success and delays.
A core benefit of contract electronics manufacturing services is streamlined production. Specialized contract manufacturers have refined workflows, automated inspection systems, and strong vendor relationships that result in faster turnaround times. BoardAssembly.com offers comprehensive solutions that include design support, material sourcing, and PCB assembly, all coordinated to meet your schedule and budget.
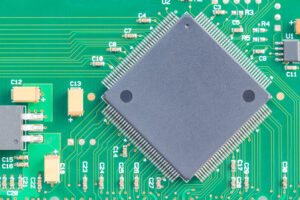 Another major advantage is improved supply chain management. Manufacturers with extensive industry experience can source components more efficiently and navigate global supply fluctuations. Contract electronics manufacturing partners monitor market conditions, secure parts early, and prevent costly production bottlenecks. This support is especially beneficial when demand spikes or tight lead times emerge.
Another major advantage is improved supply chain management. Manufacturers with extensive industry experience can source components more efficiently and navigate global supply fluctuations. Contract electronics manufacturing partners monitor market conditions, secure parts early, and prevent costly production bottlenecks. This support is especially beneficial when demand spikes or tight lead times emerge.
Contract manufacturers also enhance quality and compliance. By leveraging robust testing protocols, including in-circuit testing and functional validation, they reduce the risk of field failures. Strong quality management systems assure that products meet industry standards and client specifications. BoardAssembly’s commitment to quality means reliable outcomes you can trust.
For many organizations, outsourcing manufacturing allows internal teams to focus on core competencies such as R&D and marketing. With a trusted CEMS provider handling production logistics, engineering teams have more time to innovate. This partnership approach also fosters scalability — whether you need low-volume prototyping or high-volume production, a contract manufacturing service adapts to your needs.
When evaluating providers, look for transparent pricing, clear communication, and strong technical support. Success in electronics manufacturing depends on collaboration and continuous improvement. With data-driven insights and proactive project management, the right contract electronics manufacturing services partner supports long-term growth.
If sustainability and regulatory compliance are priorities, ensure that your contract partner adheres to environmental and industry standards. Certifications, traceability, and documented processes reflect a commitment to excellence.
In summary, contract electronics manufacturing services help businesses reduce costs, accelerate time to market, and enhance product quality. As technologies evolve and consumer expectations rise, outsourcing production to experts becomes an increasingly strategic decision. BoardAssembly.com stands ready to deliver tailored manufacturing services that align with your product goals and operational requirements.
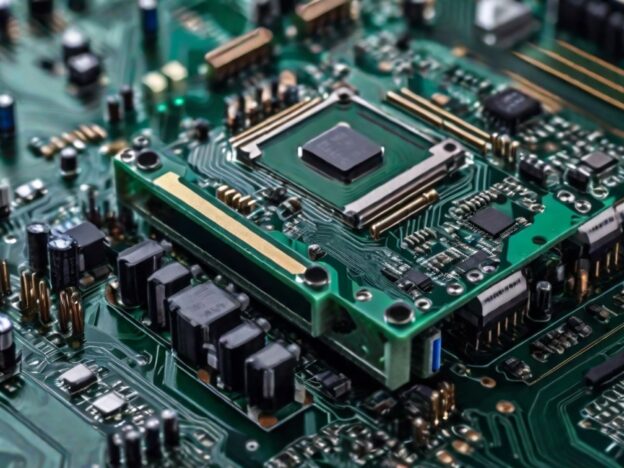
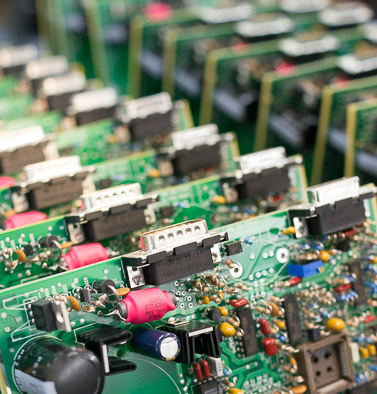

 One of the most profound benefits of turnkey assembly is integrated supply chain management. Your assembly partner handles component procurement, ensuring parts are sourced from trusted suppliers and delivered on schedule. This eliminates the burden of vendor negotiations, purchase orders, and inventory delays — common pain points for in-house manufacturing teams.
One of the most profound benefits of turnkey assembly is integrated supply chain management. Your assembly partner handles component procurement, ensuring parts are sourced from trusted suppliers and delivered on schedule. This eliminates the burden of vendor negotiations, purchase orders, and inventory delays — common pain points for in-house manufacturing teams.
 One of the primary advantages of BGA components is their enhanced electrical performance. By placing solder connections directly beneath the package, signals travel shorter distances with reduced parasitics, which boosts signal integrity. Improved thermal performance also helps distribute heat efficiently — critical for processors, FPGAs, and high-speed RF modules.
One of the primary advantages of BGA components is their enhanced electrical performance. By placing solder connections directly beneath the package, signals travel shorter distances with reduced parasitics, which boosts signal integrity. Improved thermal performance also helps distribute heat efficiently — critical for processors, FPGAs, and high-speed RF modules.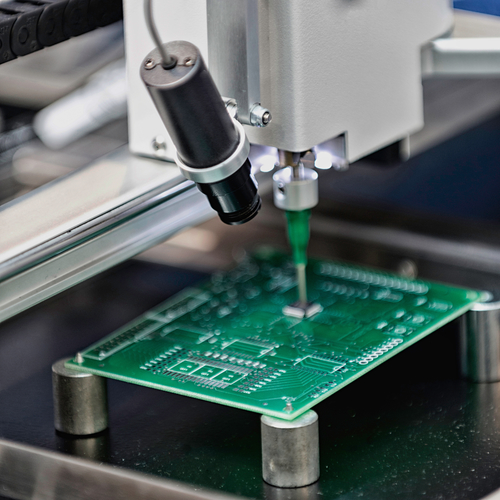
 Early in the product lifecycle, EMS providers support design for manufacturability (DFM) reviews. In this phase, engineers analyze PCB layouts and specifications to identify potential assembly issues, suggest improvements, and ensure components are optimized for manufacturing. This proactive approach minimizes costly revisions and improves end-product quality.
Early in the product lifecycle, EMS providers support design for manufacturability (DFM) reviews. In this phase, engineers analyze PCB layouts and specifications to identify potential assembly issues, suggest improvements, and ensure components are optimized for manufacturing. This proactive approach minimizes costly revisions and improves end-product quality.
 Thru-hole assembly involves inserting electronic component leads into drilled holes on a PCB and soldering them in place. This process creates mechanically robust solder joints, superior to many surface mount options when it comes to withstanding vibration and thermal stress. Industries that demand long-life performance and high reliability often favor thru-hole components like connectors, large capacitors, transformers, and tall leaded components that simply cannot be mounted using SMT alone.
Thru-hole assembly involves inserting electronic component leads into drilled holes on a PCB and soldering them in place. This process creates mechanically robust solder joints, superior to many surface mount options when it comes to withstanding vibration and thermal stress. Industries that demand long-life performance and high reliability often favor thru-hole components like connectors, large capacitors, transformers, and tall leaded components that simply cannot be mounted using SMT alone.


