 When it comes to printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, the terms “full turnkey” and “turn-key assembly” are often synonymous with efficiency, quality, and convenience. At Board Assembly, we offer comprehensive solutions that cater to every aspect of PCB production. Our full turnkey services are designed to streamline the entire process, from initial design and prototyping to final production and testing, ensuring that every product meets the highest standards of quality and reliability.
When it comes to printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, the terms “full turnkey” and “turn-key assembly” are often synonymous with efficiency, quality, and convenience. At Board Assembly, we offer comprehensive solutions that cater to every aspect of PCB production. Our full turnkey services are designed to streamline the entire process, from initial design and prototyping to final production and testing, ensuring that every product meets the highest standards of quality and reliability.
What is Full Turnkey in PCB Assembly?
Full turnkey PCB assembly refers to a process where the manufacturer, like Board Assembly, takes complete responsibility for all aspects of the production. This includes procuring the raw materials, managing the supply chain, manufacturing the PCB, and handling quality control and testing. By opting for a full turnkey solution, clients can save time and reduce costs by avoiding the need to coordinate multiple vendors or manage various stages of the assembly process.
At Board Assembly, our full turnkey services start with a detailed understanding of the client’s needs. Our team of experts collaborates closely with clients to understand their project requirements, budget constraints, and timelines. From there, we handle everything, including sourcing high-quality components from trusted suppliers. Our extensive network of suppliers ensures that we can source the best materials at competitive prices, further optimizing the cost-effectiveness of the production process.
The Advantages of Turn-key Assembly with Board Assembly
One of the key benefits of choosing Board Assembly’s turn-key assembly services is the level of control and oversight we provide throughout the entire production process. By managing every aspect of the assembly in-house, we can ensure stringent quality control measures are in place. Each PCB goes through rigorous testing and inspection phases, utilizing advanced equipment to detect any potential defects or inconsistencies. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that every circuit board that leaves our facility is of the highest quality.
control and oversight we provide throughout the entire production process. By managing every aspect of the assembly in-house, we can ensure stringent quality control measures are in place. Each PCB goes through rigorous testing and inspection phases, utilizing advanced equipment to detect any potential defects or inconsistencies. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that every circuit board that leaves our facility is of the highest quality.
Another advantage of our turn-key assembly solutions is the speed and efficiency with which projects can be completed. Because we handle every stage of the process, from design to delivery, we can significantly reduce lead times. This is particularly beneficial for companies operating in fast-paced industries where time-to-market is critical. By reducing production times without compromising on quality, Board Assembly helps clients stay competitive in their respective markets.
A Focus on Quality and Customer Satisfaction
At Board Assembly, quality is not just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental aspect of our business philosophy. Our full turnkey solutions are built around the idea of delivering superior quality products that meet or exceed customer expectations. We achieve this by implementing a robust quality management system that adheres to industry standards and continuously seeks to improve our processes.
Our commitment to customer satisfaction goes beyond just delivering a product. We provide ongoing support and services to our clients, ensuring they have everything they need to succeed. Whether it’s assistance with design optimization, troubleshooting, or after-sales support, our team is always ready to help. By choosing Board Assembly’s turn-key assembly services, clients gain a partner who is as invested in their success as they are.
Why Choose Board Assembly for Your Turn-key Needs?
Choosing a reliable partner for PCB assembly is crucial to the success of any electronic product. Board Assembly stands out in the industry due to our comprehensive full turnkey services that combine quality, speed, and cost-effectiveness. With our extensive experience and state-of-the-art facilities, we can handle projects of any size or complexity, ensuring that all your needs are met under one roof.
By opting for Board Assembly’s full turnkey solutions, you’re choosing a hassle-free, efficient, and reliable way to bring your products to life. With a proven track record and a commitment to excellence, Board Assembly is your go-to partner for all your PCB assembly needs.
For more information on how Board Assembly can support your project with our full turnkey solutions, visit our website at BoardAssembly.com and reach out to our team today.
By focusing on full turnkey and turn-key assembly services, Board Assembly provides a seamless, all-inclusive solution that enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and delivers high-quality PCBs to clients worldwide. Whether you’re a startup or an established enterprise, we have the expertise and resources to bring your vision to life with precision and excellence.
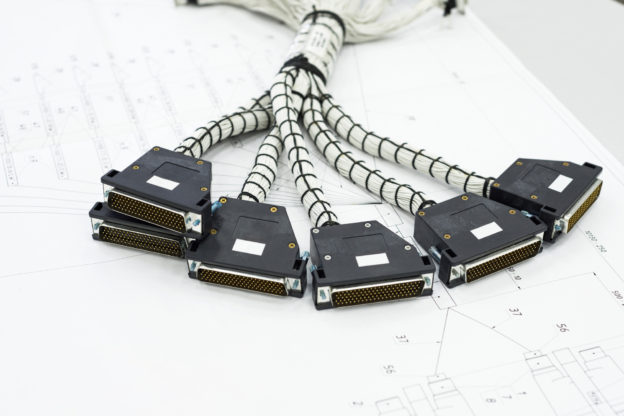

 For example, ethernet cable assemblies are designed to provide service supporting bandwidth speeds up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet, such as large data centers, military field units, and medical facilities. For those applications that require a lightweight, smaller assembly that can transmit clearly and rapidly over great distances, support greater bandwidths, with high voltage isolation, then fiber optic cable assemblies would meet those needs. A few of the industries that utilize fiber optic cable assemblies, include aerospace, automotive, industrial, medical, and military applications.
For example, ethernet cable assemblies are designed to provide service supporting bandwidth speeds up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet, such as large data centers, military field units, and medical facilities. For those applications that require a lightweight, smaller assembly that can transmit clearly and rapidly over great distances, support greater bandwidths, with high voltage isolation, then fiber optic cable assemblies would meet those needs. A few of the industries that utilize fiber optic cable assemblies, include aerospace, automotive, industrial, medical, and military applications.
 In the printed circuit board business, there are two primary ways to mount components onto the circuit board:
In the printed circuit board business, there are two primary ways to mount components onto the circuit board: 


 What Is Conformal Coating?
What Is Conformal Coating?


