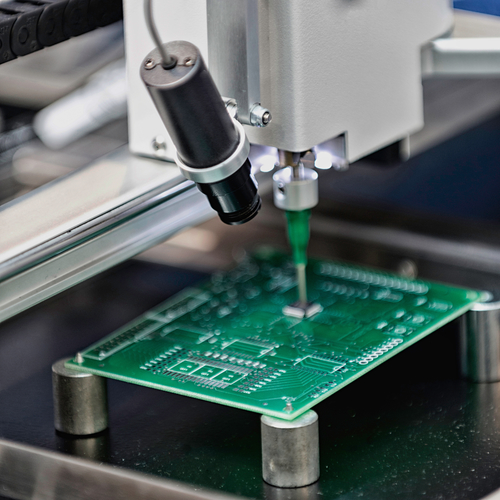
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are at the heart of nearly every electronic device we use today—from smartphones and medical monitors to aerospace controls and industrial machines. Choosing the right PCB for your specific application isn’t just about picking the cheapest option—it’s about ensuring your product functions reliably, efficiently, and safely.
So how do you know which type of PCB is right for your needs? Let’s walk through the key factors to consider when selecting a PCB during the PCB Fabrication process.
 1. Understand Your Application Requirements
1. Understand Your Application Requirements
Start by clearly identifying the role the PCB will play in your device. Ask yourself:
- Will the board be used in a high-temperature environment?
- Does it need to be flexible or rigid?
- Will it handle high frequencies or power loads?
- Are there space constraints or weight limits?
Understanding the physical and functional demands of your application will help guide your PCB design, material choices, and layout.
2. Choose the Right Type of PCB
There are several types of Printed Circuit Boards, each serving different purposes:
- Single-sided PCBs – Great for simple, low-cost electronics like calculators and toys.
- Double-sided PCBs – Common in consumer electronics where moderate complexity is needed.
- Multi-layer PCBs – Ideal for high-performance, compact designs like smartphones, servers, and aerospace tech.
- Rigid PCBs – Best for durable, permanent structures.
- Flexible PCBs – Perfect for wearables, medical devices, or curved applications.
- Rigid-Flex PCBs – Used in high-performance electronics that require both flexibility and strength.
The right type depends on both your performance needs and your product’s design limitations.
3. Select the Proper Materials
In PCB Fabrication, the choice of materials affects durability, conductivity, heat resistance, and cost. Common materials include:
- FR-4 – A widely used fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate; affordable and versatile.
- Polyimide – Offers better flexibility and heat resistance, great for aerospace and military uses.
- Ceramic – Provides high thermal conductivity and is used in high-frequency or high-power applications.
Choosing the right substrate and copper thickness is crucial to match your performance and environmental needs.
4. Consider Signal Integrity and Thermal Management
For applications involving high-speed signals or high power, signal integrity and heat dissipation become critical. Your PCB layout, trace widths, spacing, and use of thermal vias must be optimized to prevent overheating and maintain performance.
This is especially true for industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical—where failure isn’t an option.
5. Work with an Experienced Manufacturer
Your PCB is only as good as the partner who fabricates and assembles it. At BoardAssembly.com, we specialize in high-quality PCB Fabrication tailored to your application’s unique needs. Whether you’re working on a prototype or full production run, we deliver precision, reliability, and expert support throughout the process.
 Choosing the right Printed Circuit Board isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. By understanding your application, selecting the right materials, and working with a trusted manufacturer, you’ll set your project up for long-term success.
Choosing the right Printed Circuit Board isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. By understanding your application, selecting the right materials, and working with a trusted manufacturer, you’ll set your project up for long-term success.
Ready to get started? Visit our PCB Fabrication page to learn more about our capabilities or contact us to discuss your project.

 Compactness and Efficiency in Medical Technology
Compactness and Efficiency in Medical Technology Supporting the Shift to Digital Healthcare
Supporting the Shift to Digital Healthcare





